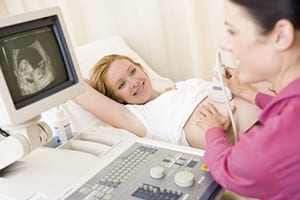
Ultrasound imaging, also called sonography, is a painless and noninvasive procedure used to visualize the inside of the human body through the use of high-frequency sound waves.
During an ultrasound, a trained technician or doctor moves a device called a transducer over part of your body; the transducer emits sound waves, which bounce off tissues and are received back as echoes. The echoes created can identify the size, structure and location of body tissues; that information is then used to create an image on the area of study.
Ultrasound is the most utilized form of diagnostic imaging after general x-ray, largely because no radiation is involved, making it the preferred imaging modality for diagnosis and monitoring of pregnant women and fetuses.
It is also frequently used for breast, cardiac, renal, liver, gallbladder, musculo-skeletal, ophthalmic, testicle, salivary gland and lymph node imaging among many others.
Additionally, ultrasound serves as a guiding tool for interventional procedures such as fine needle breast aspiration and biopsy
Fully Accredited by the
American College of Radiology




